Discriminant analysis is an essential statistical tool that can be used when you have got a set of records / respondents which are classified into some segments or clusters and you need to predict the segment for a new respondent or set of respondents:
- discriminant analysis allows identifying a set of key variables that are most differentiating with respect to these segments / clusters;
- discriminant analysis also allows assessing the relationships between these key variables and the clusters, so that
- the user can statistically assign a new record / respondent to the most likely cluster it belongs to, according to its answers / observed values on these key variables.
These key selected variables and relationships are then translated into a set of rules used by a platform (usually referred to as segmentation typing tool or allocation tool) that enables its user to predict the most likely segment a record / respondent belongs to.
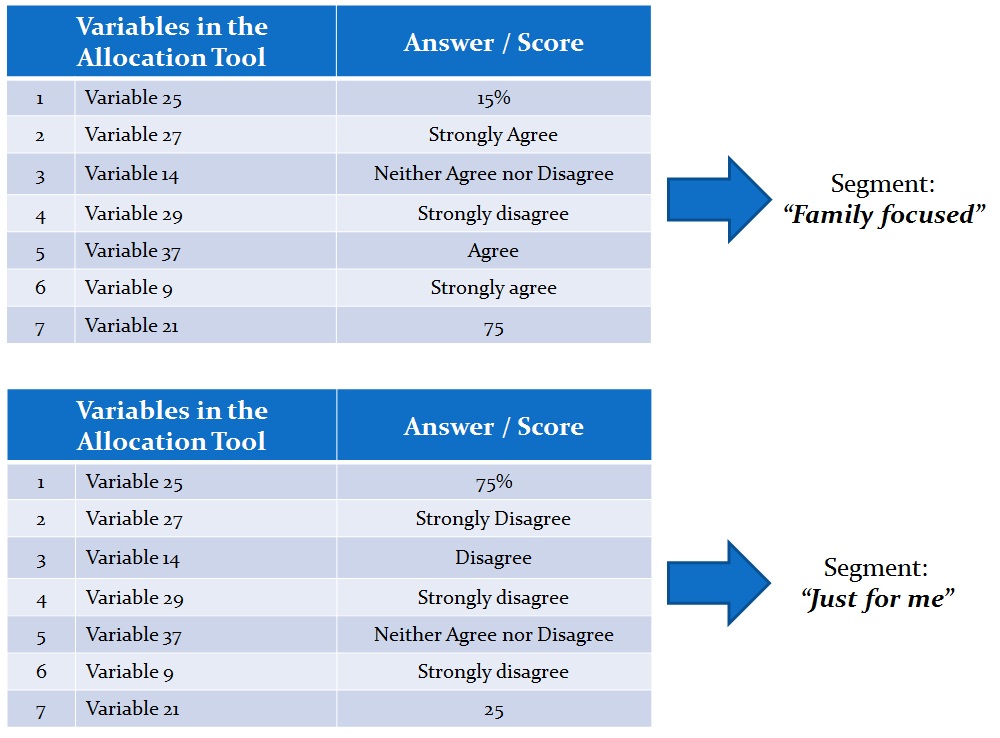
In order to ensure long-term success of a segmentation project, the typing tool should:
- be characterized by a limited number of questions (e.g., 5-6 variables in a tool to be distributed among medical representatives; 8-12 variables in a tool used to allocate respondents in a follow-up research project);
- have the questions carefully selected – predictive accuracy should be maximized;
- be able to predict the most likely segment with the lowest classification error;
- be built via a robust discriminant-type algorithm with cross-validation;
- be deployed on a user-friendly platform.
